Chmod command example 123293-Chmod command example in unix
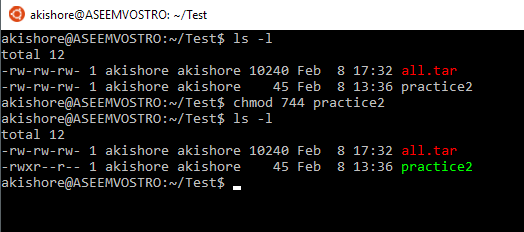
chmod examples using octal mode First column shows the chmod command , second column shows how the value is calculated for the permission last columns of owner, group, others shows individual octal values and actual bit set on file as seen by ls l For setting any other permission combination for owner, group & other , pick corresponding Chmod Examples in Linux / Unix 1 Give read, write and execute permissions to everyone Read, write and execute 421=7 $ chmod 777 samplesh In the above example, you can see that the permissions are specified with a three digit number The first digit is for user permissions, second is for group and third is for others permissionThe Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode chmod has two operating modes symbolic mode;
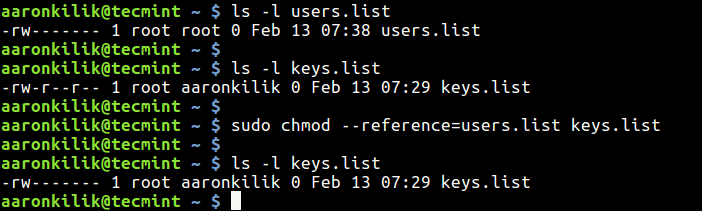
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux
Chmod command example in unix
Chmod command example in unix-To change the file permission of multiple files, specify the file pattern with the chmod command For example, if we want to set read and write permission for all text files, specify the * txt pattern with chmod commandExamples Deny execute permission to everyone chmod ax file Allow read permission to everyone chmod ar file Make a file readable and writable by the group and others chmod gorw file Make a shell script executable by the user/owner $ chmod ux myscriptsh You can then execute it like this /myscriptsh
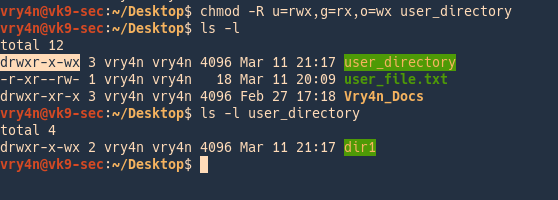



File Permissions In Linux Unix Vk9 Security
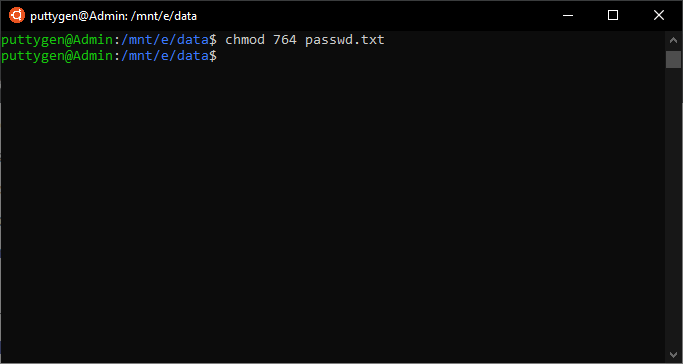
Now, let us see how chmod command can be used to change the access mode of a file Example 1 Let's change the assgn1_clientc permission so that the owner cannot write(w) in the file but can only read it BEFORE rwrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc COMMAND chmod u=r assgn1_clientc AFTER rrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc BeforeChmod ux file1 To remove the write permission for others for file2 chmod ow file2 You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone chmod ugo=rx file3 The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be expressed as chmod a=rx file3 ForChmod options mode file_name You can change permissions using alphanumeric characters (arwx) or with octal numbers (777) Here's a chmod example using for setting permissions so that Owner can read, write and execute Group can read, write and execute
The syntax is something like this $ chmod u/permissions g/permissions o/permissions fileor /dir/ So, if I run $ chmod 777 file rwx rwx rwx everybody can do anything with file Or I run $ chmod 744 dir rwx r r only user can read, write and execute, group and others only read dir Examples To Change group ownership In our case I am using group1 as a group in the system To change ownership we will use chown group1 file1txt You can see that the group permissions changed to group1 from root, if you use v option it will report that We just need to add a "" to change groupIn Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call used to change the access permissions of file system objects sometimes known as modes It is also used to change special mode flags such as setuid and setgid flags and a 'sticky' bit The request is filtered by the umask The name is an abbreviation of change mode They are shown when listing files in long
6 Read write permissions 4 Read only permissions 0 No permissions u Owner permissions, used with r or w g Group permissions, used with r or w o Other user permissions, used with r or w a chmod command or "change mode command", and as that name implies, the chmod command is used to change the mode of Unix/Linux files In other words it is used to define the way a file can be accessedChmod 775 Chmod 775 (chmod arwx,ow) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute (G)roup can read, can write and can execute (O)thers can read, can't write and can execute



3




Freebsd Find The Chmod Numerical Value For A File Or Directory Nixcraft
Table 1069 lists the syntax options for the chmod command Table 1069 Options for the chmod command Option Description;Now, let's check out some examples of using the chmod command with symbolic form in Linux Example 1 Setting "read by owner only" file permission using chmod command In this example, we will change the file permissions of "testfile" so that only the owner can read it Other than this permission, no other group or user can read, write or execute this file In this example we add permission to the user to execute pingtxt $ chmod ux pingtxt Remove File and Folder Access Permission between role and permission is used to remove permission for the given role In this example we remove users execute permission from file pingtxt $ chmod ux pingtxt Copy Permissions From Other File




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
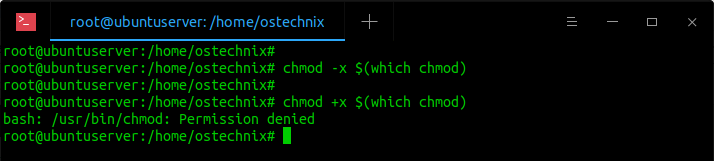



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
The following chmod command modifies the mock file, exampletxt, so that the owner (user) as well other users (group, other) receive writing and reading rights $ chmod ugorw exampletxt mixed Referencing all the user classes (a) is a possible alternative $ chmod arw exampletxt mixed Below are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode Give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it chmod g=r filename; We want the user dave to have read and write permissions and the group and other users to have read permissions only We can do using the following command chmod u=rw,og=r new_filetxt Using the "=" operator means we wipe out any existing permissions and then set the ones specified let's check the new permission on this file ls l new_filetxt




Linux Permissions Posix Chmod Chown Chgrp Youtube
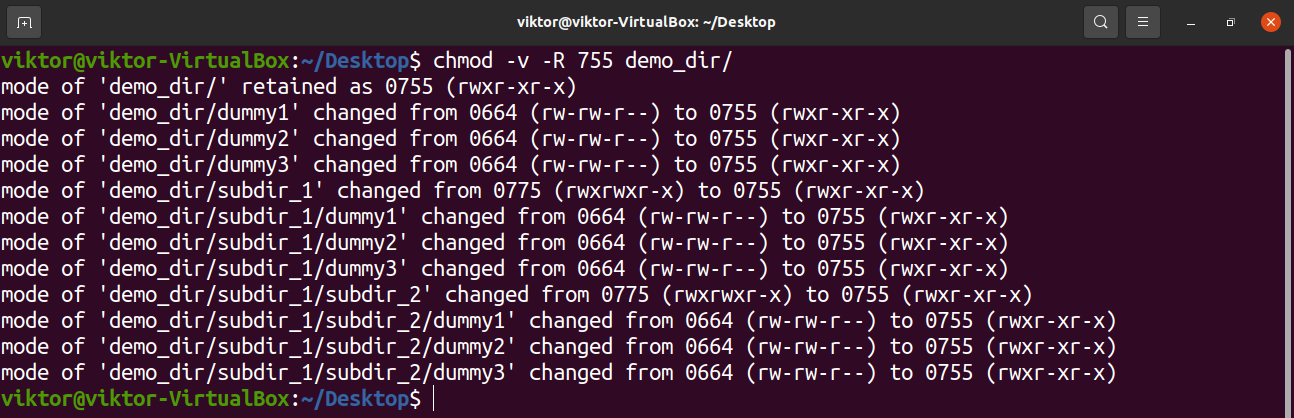



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It
To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rulesChmod Command Examples in Linux By admin The chmod command enables you to modify the permissions of a file or directory Only the owner of the file or directory or the system administrator can change the permissions of the objectGive an example Command name chgrp Full English name of the command change file group ownership Command path /bin/chgrp Execution Authority all users Command function modify the group to which the file or directory belongs Syntax Chgrp user group file or directory
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux




What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper
Chmod gowx mydir This denies group members and others the permission to create or delete files in mydir ( gow) and allows group members and others to search mydir or use it in a path name ( gox ) This is equivalent to the command sequence chmod gw mydir chmod ow mydir chmod gx mydir chmod ox mydir The chmod command can be used with both letter permissions or value permissions For example, we can specify the read and write permission with the w and r letters We can also use the digit presentation by summing the read and write values 42 = 6 We can use digit 6 to express read and write permission The other way is terminal , where you can change the permission via Chmod If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions ie to make file readable, writable and executable by everyone chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation chmod is a command to change permission of a file It stands for change mode




How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux




Hdfs Commands Hdfs Permissions And Hdfs Storage Managing Hdfs Through The Hdfs Shell Commands Informit
The chmod Command The chmod (Change Mode) command lets you apply permissions to files chmod 777 So, running chmod 777 /path/to/file/or/folder will give the file or folders owner (user), group (users within the group), and others (everyone else on the system) full read, write and execute privileges chmod R 777 /path/to/file/or/folderThe chmod command might not be the one that you may require on daily basis, but it's an extremely useful/important tool that you should know about Here, in this tutorial, we have discussed most of the basics related to this tool, and the examples we've discussed are aimed at making those basics clearTo have combination of permissions, add required numbers For example, for read and write permission, it is 42 = 6 3 chmod Examples Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 2 1 = 7 $ chmod 777 filetxt (or) $ chmod ugorwx filetxt Give execute privilege to user




Ownership And Permissions




Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
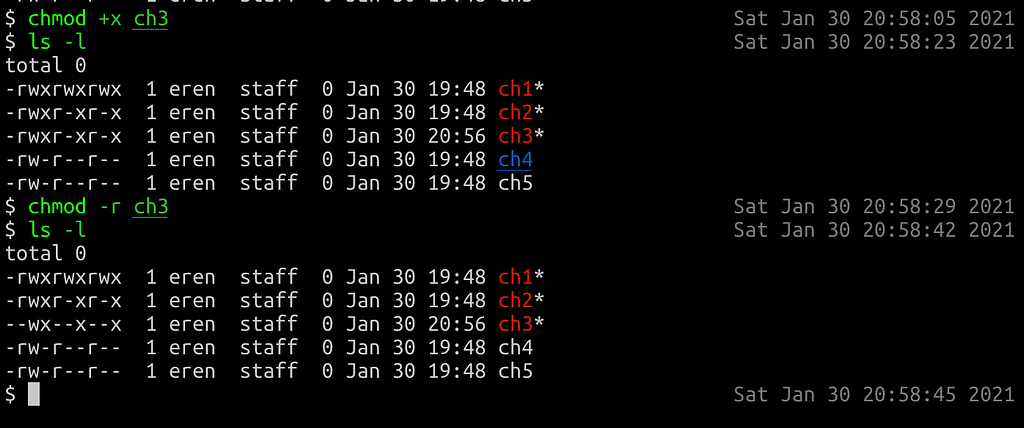
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the R, ( recursive) option The general syntax to recursively change the file's permissions is as follows chmod R MODE DIRECTORYWrite 0=2 w execute 001=1 x Perform chmod recursive with R or recursive If all your files and directories are under one parent directory then you can directly use chmod R to assign the permission recursively The syntax to modify the file and directory permission recursivelyRemove the execute permission for all users chmod ax filename;




7 Examples Of Command Chmod On Linux And Explanation



Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
Recursively remove the write permission for other users chmod R ow dirname In this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/dataphp See "how to use change user rights using chomod command" for more information Conclusion We explained the chown and chmod command forChmod command in linux with examples Chmod means 'change mode' and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed) You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unixlike systems such as linux or BSD




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
The command named "chmod" is used to set, add or remove permissions for a file or directory The chmod command can be used in any of the following ways Any combination of u,g,o and a may be used on the left and any combination of r, w and x may be used on the right Write the appropriate chmod command for each of the following desired actions




Chmod Command Examples Of Use Chmod Command Examples Of Using The Resolution Command For The Linux 777 Folder




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



Top 50 Linux Commands With Example




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




Chmod Folder Online Discount Shop For Electronics Apparel Toys Books Games Computers Shoes Jewelry Watches Baby Products Sports Outdoors Office Products Bed Bath Furniture Tools Hardware Automotive Parts Accessories



Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples



Echolink Ru Irlp Nodeop Notes Ag0n



50 Chmod Command Example In Unix ただの車



Unix Commands Chmod Linux Commands Mac Commands Laptrinhx




The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up




Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples




Chmod 777 Tutorial The Electric Toolbox Blog




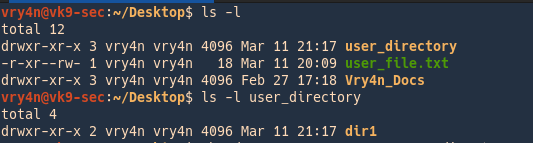
File Permissions In Linux Unix Vk9 Security




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




How To Recursively Change File Permissions In Linux Make Tech Easier



File Permissions In Linux Unix Vk9 Security
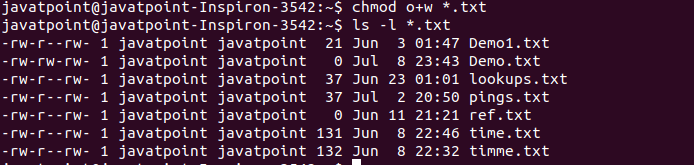



Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint



1
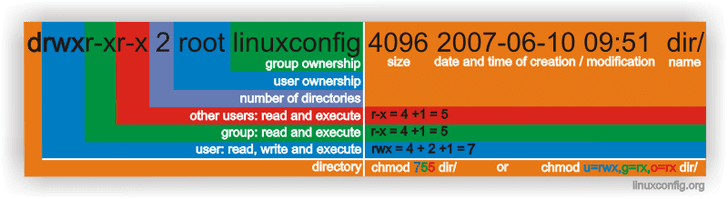



Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Linux Command Line Tutorial




Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command




How To Recursively Change File Permissions In Linux Make Tech Easier




Chmod Command Utility Software Computer File



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Using Chmod Recursively In Ubuntu Ubuntu Config
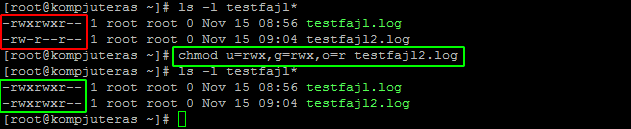



How To Display File Permissions In Octal Format In Linux Kompjuteras
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)



ベストコレクション Chmod 777 Command In Linux With Examples 無料の車の画像




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Linux Command Line Tutorial




File Chmod Gnu Png Wikimedia Commons
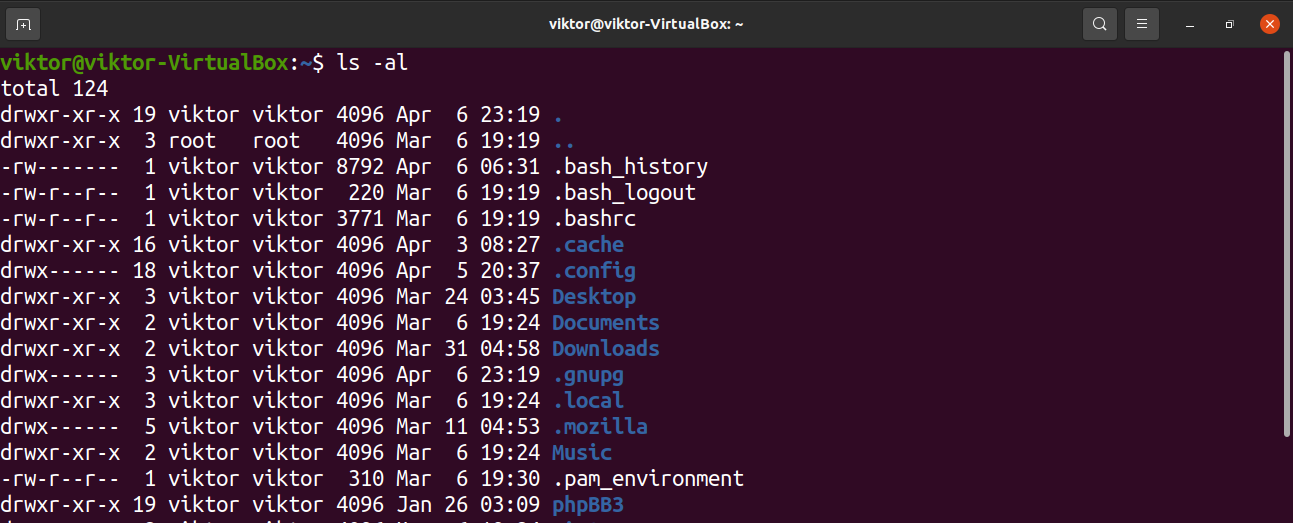



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
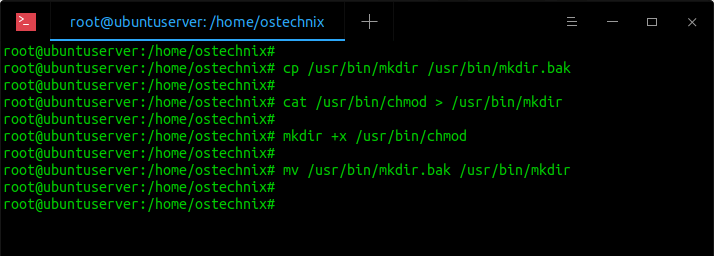



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix



Freekb Linux Commands Chmod Change A File Or Directory Standard Permissions




Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples Linuxtect




How To Change Linux S Permissions Through A Practical Example Of The Chmod Command
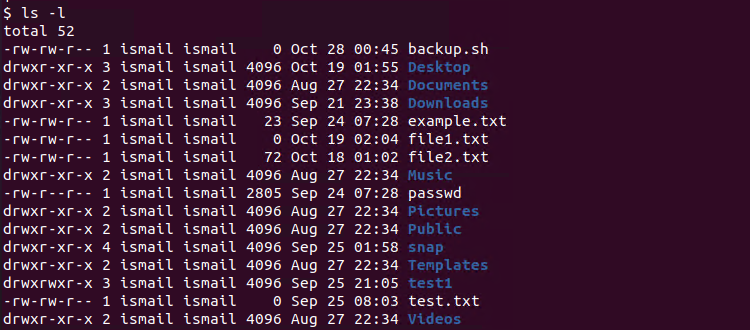



What Is Chmod X Command In Linux Linuxtect




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks
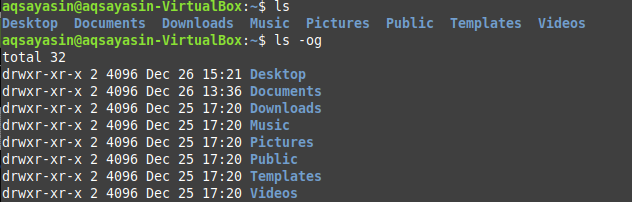



Linux Chmod Command Tutorial For Beginners




Chmod Linux Example Undiscretion Chipmunkhollow Biz




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




How Does The Number 777 Come Out In Chmod 777 Under Linux Develop Paper




Linux Chmod Command



Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf
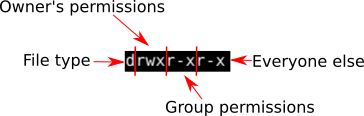



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples




Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command In Linux
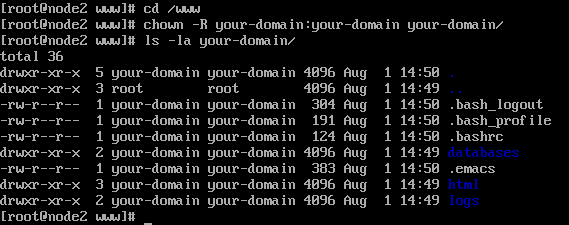



Chown Command In Linux Unix Explained With Examples The Linux Juggernaut




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
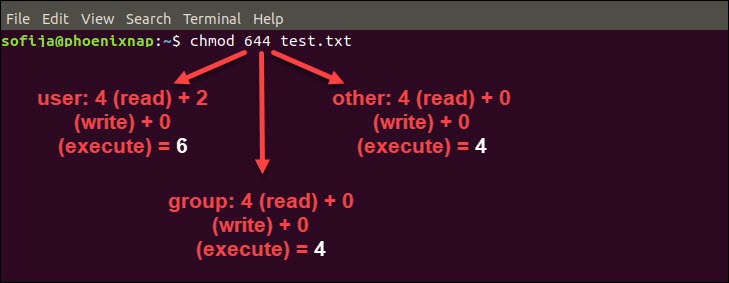



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission




Linux File Permission Explained In Easy Language




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft



3
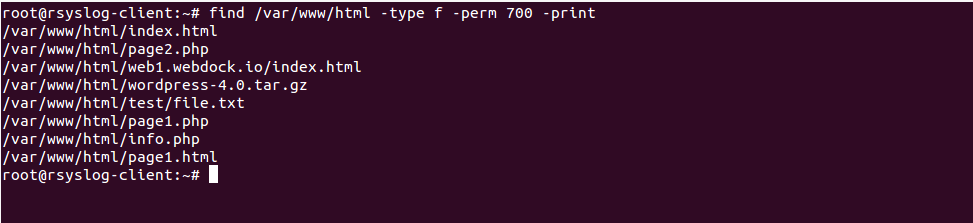



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders



Linux Permissions




Chmod Command
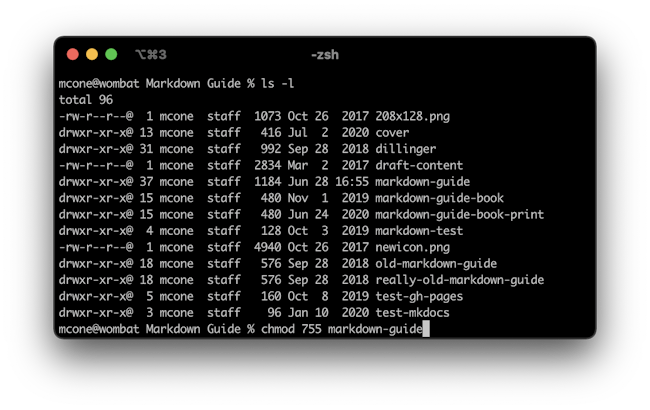



How To Set File Permissions On A Mac Macinstruct



Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com
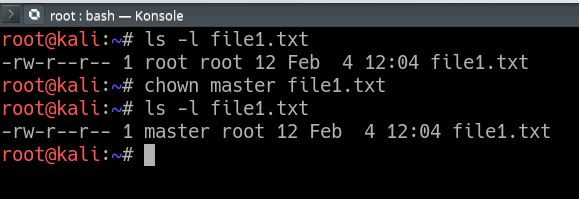



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders



Common Bash Commands




Understand Linux System File Permission



Using Terminal To Set File Permissions Amsys




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Chmod Command Linux Tutorial Syntax And Examples How To Use Chmod




Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode




In Java How To Set File Permission On A File Using Posixfilepermission Understanding Chmod Command Crunchify




7uuo3urmvl585m




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather
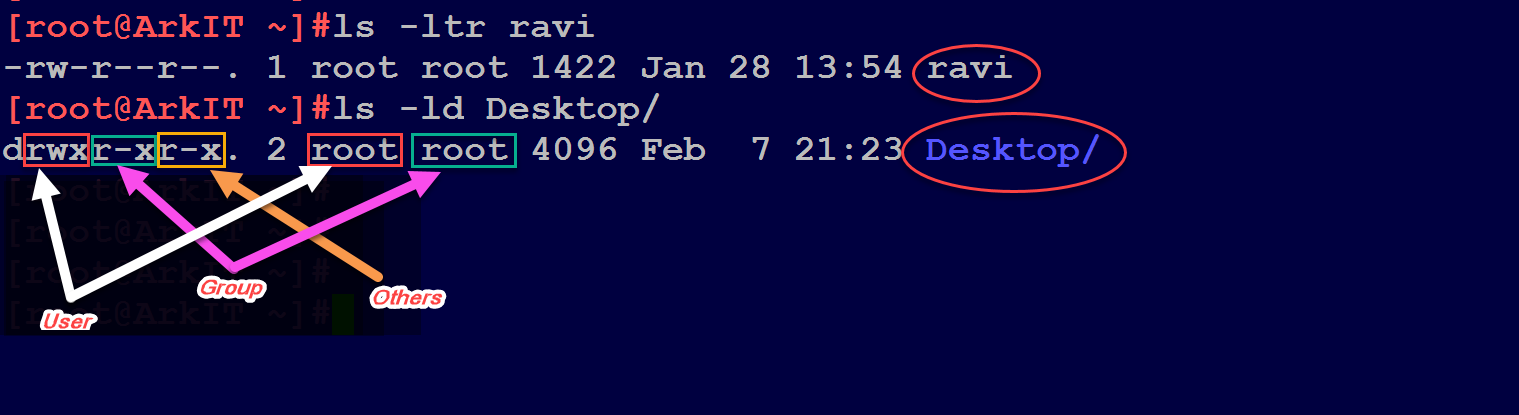



Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions




11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub



So You Can Control The Permissions Of Files And Folders On Your Server



How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Youtube




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize




Javarevisited 10 Examples Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
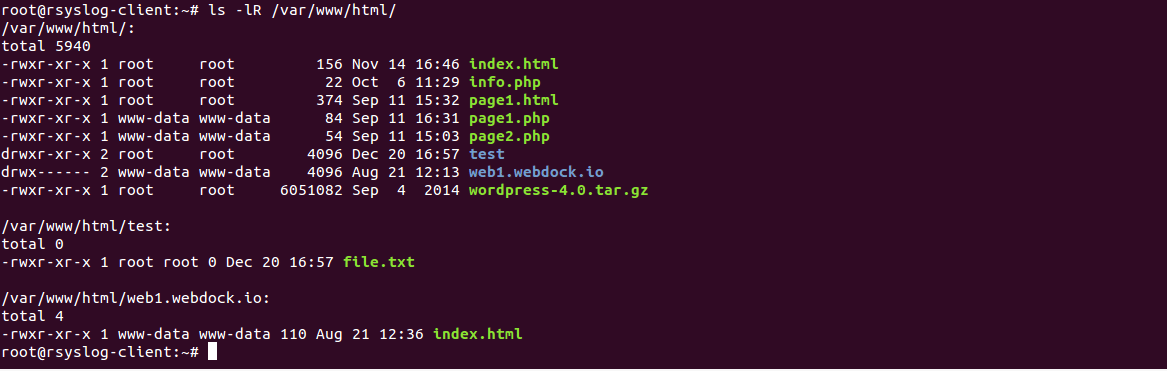



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux The Wise Bulb




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




Basic Chmod Examples



Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf




Chmod And Chown For Wordpress
コメント
コメントを投稿